My objective is to simplify and clarify economics, making it accessible to everyone. It is important to remember that the opinions expressed in my writing are solely my own and should not be considered as financial advice. Any potential losses incurred from acting upon the information provided in my writing are the responsibility of the individual, and I cannot be held liable for them.
Translate
Friday, March 29, 2024
Understanding the Pulse of America's Debt: An Analysis of Loan Delinquency Rates
Wednesday, March 27, 2024
Analyzing the Pulse of the Banking Sector: A Deep Dive into Recent Trends
In the ever-evolving landscape of the financial world, keeping a keen eye on banking trends can reveal much about the broader economic environment. Recent data on the banking sector presents a mixed bag of growth, contraction, and shifts that could have significant implications for investors, policymakers, and the economy at large. Here, we dissect the latest monthly and annual percentage changes across a range of banking metrics to understand the current state of play.
A Snapshot of Bank Credit Dynamics
Bank credit serves as the backbone of economic activity, fueling everything from business expansion to consumer spending. The latest figures show a modest monthly increase of 0.29% in bank credit across all commercial banks, albeit paired with a slight annual decline of 0.85%. This indicates a cautious lending environment, possibly reflecting banks' risk assessments amid economic uncertainties.
Securities within Bank Credit: A Closer Look
The composition of bank credit reveals significant variances. Securities in bank credit saw a slight monthly decrease of 0.02%, with a more pronounced annual drop of over 7%. This decline is even steeper in the subset of "Other Securities," plummeting by nearly 11.83% annually, suggesting a shift away from riskier assets.
Treasury and Agency Securities: The Safe Haven?
Contrasting the overall trend in securities, Treasury and agency securities experienced a modest uptick of 0.17% monthly, despite a 5.8% annual fall. This could indicate a flight to safety among banks, as these are typically considered lower-risk investments.
The Loan Portfolio: A Mixed Bag
The loan portfolio offers a brighter picture, with loans and leases in bank credit rising by 0.42% over the month and nearly 2% annually. Real estate loans, both residential and commercial, are on an upward trajectory, reflecting the ongoing demand in the housing market. Notably, consumer loans related to credit cards and other revolving plans surged by nearly 1% monthly and an impressive 9% annually, hinting at robust consumer spending.
Auto Loans: A Slight Skid
In contrast, automobile loans saw a dip, decreasing by 0.24% monthly and over 4% annually. This could be a sign of cooling demand in the auto sector or tighter lending standards.
Other Loans, Cash Assets, and Beyond
Other loans and leases painted a positive picture, growing by 0.6% monthly and 3.38% annually, showcasing diverse lending activities. Remarkably, cash assets in all commercial banks witnessed a slight monthly increase but a substantial annual jump of 14.4%, possibly reflecting liquidity preferences.
Total Assets and Liabilities: Steady as She Goes
On the balance sheet, total assets and liabilities maintained steady growth, with total assets increasing by 0.24% monthly and 1.43% annually. This balanced growth is mirrored in total liabilities, ensuring a stable financial footing for the sector.
The Deposit Dilemma and Borrowings Boost
Interestingly, deposits showed a minimal monthly increase but an annual decline, suggesting changing consumer and business preferences in managing their cash. Conversely, borrowings by banks saw a slight monthly decrease but skyrocketed annually by over 22%, indicating banks are leveraging external financing to bolster their operations.
Conclusion: A Sector in Flux
The banking sector remains a critical barometer for the economy. The latest data points to a sector adjusting to a complex web of challenges and opportunities. While there are areas of strength, particularly in consumer lending and cash assets, the shifts in securities and certain loan categories underscore a cautious approach to risk. As the sector navigates through these turbulent times, its adaptability and resilience will be key to sustaining growth and stability.
Tuesday, March 26, 2024
Strategic Petroleum Reserve
It provides a comprehensive analysis of the Strategic Petroleum Reserve (SPR) drawdowns in response to the Russian invasion of Ukraine and their potential implications. It covers several key points:1. The Biden administration released a record 370 million barrels from the SPR, accounting for 64% of the reserve's stock as of February 2022, to counter oil price hikes due to the Russian invasion.2. While the releases likely helped lower gasoline prices to some extent, the impact was relatively small, amounting to only 1.6% of global oil production during that period.3. The drawdowns had redistributory effects, benefiting consumers but potentially harming the oil industry and those with investments in it.4. The passage raises the question of the SPR's purpose – whether it should function as a price stabilization tool through speculative trading or be reserved strictly for emergencies.5. It also questions the need for an SPR given the U.S.'s status as a net oil exporter, though the validity of this argument depends on the stability of U.S. production and private storage facilities.It presents a balanced analysis, highlighting the potential benefits and drawbacks of the SPR releases, as well as the broader debate surrounding the reserve's role and relevance in the current energy landscape.
Thursday, March 21, 2024
Analyzing the Latest Trends in the Real Estate Market: A Look at Monthly and Annual Changes
March 21, 2024
In today's dynamic real estate market, understanding the latest trends is crucial for investors, homeowners, and market analysts alike. Recent data has shed light on some intriguing shifts in both the monthly and annual performance of various segments of the market. In this blog post, we dive into these trends, presenting a detailed analysis of the latest percentage changes in existing home sales, housing inventory, median sales prices, and more.
Monthly Insights
Starting with the monthly changes, we see a mixed bag of results that offer a nuanced view of the market's immediate direction. Notably, existing single-family home sales have shown a significant uptick, with a 10.3% increase. This is closely followed by the overall existing home sales, which have risen by 9.5%. On the inventory side, the existing home sales housing inventory saw a 5.9% increase, suggesting a slight easing in the tight supply that has characterized the market.
However, not all changes were positive. The existing home sales months supply experienced a decrease of 3.3%, indicating that despite an increase in inventory, the pace at which homes are selling is still outstripping new listings. This could signal continued competitive conditions for buyers.
Annual Perspectives
When we expand our lens to the annual changes, a longer-term perspective emerges that contrasts with the monthly view. The most striking figure is the existing single-family home sales months supply, which has increased by 12.0% compared to last year. This suggests that while the market remains competitive, there is a gradual move towards a more balanced state between buyers and sellers.
Interestingly, the annual data also highlights a resilience in pricing, with the median sales price of existing homes growing by 5.7% year over year. This growth, albeit slower than in previous years, underscores the underlying strength of the market and the continued demand for housing.
Visualizing the Data
To bring these insights to life, we've visualized the data in two comprehensive bar charts. The first chart details the latest monthly percentage changes, showcasing the immediate shifts across different market segments. The second chart offers a look at the annual percentage changes, providing a broader perspective on the market's trajectory over the past year.
Implications and Outlook
The data presents a picture of a real estate market that is in flux, balancing between the pressures of demand, supply, and pricing. For buyers, the slight increase in inventory and the moderating price growth could offer more opportunities in the coming months. Sellers, on the other hand, continue to benefit from favorable conditions, especially in sought-after areas where supply constraints persist.
As we move further into 2024, the real estate market will undoubtedly continue to evolve. Market participants will need to stay informed and agile, ready to adapt to the latest trends and data. Whether you're looking to buy, sell, or simply keep a pulse on the market, understanding these dynamics is key to navigating the complexities of real estate today.
In summary, while challenges remain, the latest data offers hopeful signs for a more balanced market ahead. By keeping a close eye on these trends, stakeholders can make informed decisions that align with their goals and the realities of the current real estate landscape.
Wednesday, March 20, 2024
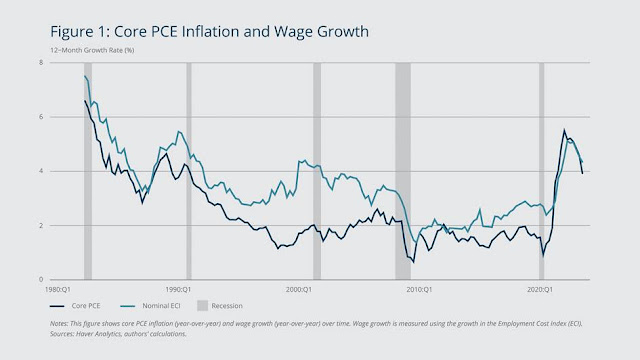
Core PCE Inflation and Wage Growth
PCE and nominal wage growth rates tend to move simultaneously. As wages grow, consumers have more money to spend, which can lead to an increase in PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures). The data shows that wage growth rates were around 4% before the internet bubble collapsed in the early 2000s. Prior to the financial crisis, wage growth rates stayed around 3%.
The blue line represents the Core PCE Inflation rate, which measures inflation excluding food and energy prices. The line exhibits significant fluctuations over the years, peaking around the early 1990s and late 2000s, while reaching lower levels in the mid-2000s and late 2010s.
The orange line depicts Nominal Wage Growth, which appears to follow a smoother trend compared to the inflation rate. Wage growth generally remained below the inflation rate during periods of high inflation but exceeded inflation during periods of lower inflation.
The gray bars indicate periods of recession in the US economy. Notably, both inflation and wage growth tend to decline during recessionary periods.
The plot effectively illustrates the historical relationship between inflation and wage growth, highlighting the periods when they diverged or converged, and how they were impacted by economic cycles.
Navigating the Cryptocurrency Landscape: Financial Literacy, Risk Tolerance, and Ownership Trends
Cryptocurrencies have carved out a significant niche in the financial ecosystem, evolving from a novel concept to a widely recognized asset class. Amidst this rapid growth, the study by Fumiko Hayashi and Aditi Routh titled "Financial Literacy, Risk Tolerance, and Cryptocurrency Ownership in the United States" offers invaluable insights into the dynamics of cryptocurrency ownership, emphasizing the crucial roles of financial literacy and risk tolerance. Published in March 2024, this research sheds light on the diverse profiles of cryptocurrency owners and the implications for policy and education.
The Study's Core Findings
The research divides cryptocurrency owners into three distinct categories based on their primary purpose: investment, transactions, and a mix of both. This categorization is pivotal, revealing nuanced differences in financial literacy and risk tolerance among these groups compared to non-owners. Here are some key takeaways:
Investors and Mix Users: These groups are identified as having higher levels of financial literacy and risk tolerance than those who do not own cryptocurrencies. This distinction underscores the importance of these traits in navigating the volatile cryptocurrency market effectively.
Transactors: Surprisingly, this group exhibits lower financial literacy compared to non-owners but possesses a slightly higher risk tolerance. The unique position of transactors highlights a potential area of financial vulnerability, especially given the lack of consumer protections in the cryptocurrency domain.
Demographic and Financial Characteristics: The study also delves into the demographic and financial attributes of each group, revealing that transactors, in particular, might be more financially vulnerable. This vulnerability stems from factors like lower financial literacy, minority status, and lower credit scores.
Implications for Policy and Education
The findings of Hayashi and Routh's research carry significant implications for policymakers, educators, and financial advisors. As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, understanding the diverse profiles of cryptocurrency owners can inform targeted consumer protection and financial education efforts. Particularly, the study highlights the need for:
Enhanced Consumer Protections: For transactors, who may use cryptocurrencies for day-to-day transactions, the absence of consumer protections poses a significant risk. Policymakers could consider regulations that safeguard these users, such as clearer disclosures and transaction reversal mechanisms.
Focused Financial Education: The varied levels of financial literacy across owner groups underscore the importance of tailored financial education programs. Such initiatives could aim to improve understanding of cryptocurrency risks, especially among potential transactors and new investors.
Awareness and Research: The study also calls for continued research into the cryptocurrency space, particularly regarding the impacts of enhanced consumer protections and financial education. As the market matures, ongoing analysis will be essential to adapt policies and educational efforts to the evolving landscape.
Conclusion
The exploration of financial literacy, risk tolerance, and cryptocurrency ownership by Hayashi and Routh provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of cryptocurrency in the United States. Their work not only contributes to the academic understanding of this asset class but also offers practical guidance for policymakers and educators looking to navigate the complexities of the cryptocurrency market. As we move forward, these insights will be invaluable in fostering a safer, more informed, and inclusive cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Navigating the Waters of Commercial Real Estate in the Pandemic Era: Insights from Lease Expirations
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a catalyst for change across numerous sectors, but perhaps one of the most significantly impacted has been the commercial real estate (CRE) market. A recent study sheds light on how lease expirations have influenced CRE property performance, with a particular focus on the dramatic shifts observed during the pandemic. This blog dives into the key findings of this study, exploring the ramifications for property owners, investors, and lenders in the evolving landscape of CRE.
Pre-Pandemic Lease Expirations: A Sign of Things to Come
Before the world had ever heard of COVID-19, lease expirations in the CRE sector were already a harbinger of potential risk, particularly in weaker markets. Properties facing expiring leases could expect notable increases in vacancy rates and dips in net operating income (NOI), revealing an inherent vulnerability in the CRE market to shifts in lease dynamics. However, these pre-pandemic observations were just the tip of the iceberg compared to the upheavals that were to come.
The Pandemic's Amplification of Lease Expiration Effects
With the onset of the pandemic, the already precarious situation for properties with expiring leases worsened, especially for office spaces. The study highlights that the adverse effects of lease expirations on office occupancy surged by more than 50% overall during the pandemic, with a doubling of this impact for offices located in central business districts (CBDs). This phenomenon is attributed to the pandemic-induced shift towards remote work, leading to a sustained decline in demand for office spaces, particularly in CBDs where the effects were most pronounced.
The study underscores the vulnerability of the office sector to the pandemic's disruptions, pointing to a potentially grim future as leases continue to expire in the coming years. This is especially true for CBD office spaces, which face the dual challenges of evolving work habits and the resultant diminishing demand for physical office locations.
Lender Exposure to At-risk Office Markets
An intriguing aspect of the study is its examination of how different types of lenders are exposed to these at-risk office markets. Nonbank and large bank lenders, according to the study, have higher exposures to distressed CBD office loans compared to their regional and community bank counterparts. This disparity highlights a crucial dimension of risk distribution across the financial ecosystem supporting the CRE market, suggesting that the impact of declining office property performance may be unevenly felt across the lending landscape.
Implications and the Road Ahead
The findings of this study bear significant implications for stakeholders in the CRE market. Property owners, particularly those with investments in office spaces in CBDs or areas with high remote work adoption, need to brace for continued challenges. The shifting dynamics call for innovative strategies to repurpose or reimagine office spaces to align with the new normal of work and urban life.
For investors, the heightened risk associated with lease expirations during the pandemic era underscores the importance of due diligence and the need for diversified investment strategies that account for the changing landscape of demand for commercial spaces.
Lenders, especially nonbank and large bank entities, must navigate the increased exposure to at-risk markets with caution, balancing support for the CRE sector with prudent risk management to mitigate potential losses.
In conclusion, the CRE market stands at a crossroads, with the pandemic accelerating changes in work habits and consequently, the demand for commercial spaces. The insights from lease expirations during this period offer a valuable lens through which to view the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Adapting to this new reality will require flexibility, innovation, and a deep understanding of the evolving market dynamics that the pandemic has set in motion.